TIbq25504高效率超低功耗能量采集解決方案
Texas Instruments introduces highly efficient boost charger IC for nano power energy harvesting
The bq25504 is the first of a new family of intelligent integrated energy harvesting Nano-Power management solutions that are well suited for meeting the special needs of ultra low power applications. The product is specifically designed to efficiently acquire and manage the microwatts (μW) to miliwatts (mW) of power generated from a variety of DC sources like photovoltaic (solar) or thermal electric generators. The bq25504 is the first device of its kind to implement a highly efficient boost converter/charger targeted toward products and systems, such as wireless sensor networks (WSN) which have stringent power and operational demands. The design of the bq25504 starts with a DCDC boost converter/charger that requires only microwatts of power to begin operating.
bq25504主要優(yōu)勢和特性:
? Ultra Low Power With High Efficiency DC/DC Boost Converter/Charger
–Continuous Energy Harvesting From Low Input Sources: VIN ≥ 80 mV(Typical)
–Ultra Low Quiescent Current: IQ 330 nA (Typical)
–Cold-Start Voltage: VIN ≥ 330 mV (Typical)
? Programmable Dynamic Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT)
– Integrated Dynamic Maximum Power Point Tracking for Optimal Energy Extraction From a Variety of Energy Generation Sources
–Input Voltage Regulation Prevents Collapsing Input Source
? Energy Storage
–Energy can be Stored to Re-Chargeable Li-ion Batteries, Thin-film Batteries, Super-Capacitors, or Conventional Capacitors
? Battery Charging and Protection User Programmable Undervoltage /Overvoltage Levels
– On-Chip Temperature Sensor with Programmable Overtemperature Shutoff
? Battery Status Output
–Battery Good Output Pin
–Programmable Threshold and Hysteresis
–Warn Attached Microcontrollers of Pending Loss of Power
–Can be Used to Enable/Disable System Loads
bq25504應(yīng)用:
? Energy Harvesting
? Solar Charger
? Thermal Electric Generator (TEG) Harvesting
? Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN)
? Industrial Monitoring
? Energy Storage
? Environmental Monitoring
? Bridge / Structural Health Monitoring (SHM)
? Smart Building Controls
? Portable and Wearable Health Devices
? Entertainment System Remote Controls
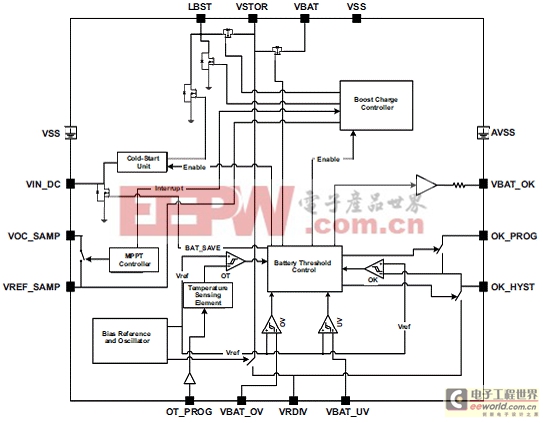
圖1.bq25504功能方框圖
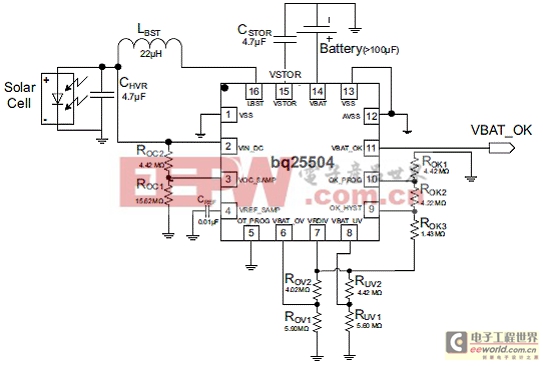
圖2.bq25504太陽能應(yīng)用電路圖
VIN_DC = 1.2 V, CSTOR= 4.7 μF, LBST= 22 μH, CHVR= 4.7 μF, CREF= 10 nF, TSD_PROTL (65°C), MPPT (VOC) = 80% VBAT_OV = 3.1 V, VBAT_UV = 2.2 V, VBAT_OK = 2.4 V, VBAT_OK_HYST = 2.8 V, ROK1 = 4.42 MΩ, ROK2 = 4.22 MΩ, ROK3 = 1.43 MΩ, ROV1 = 5.9 MΩ, ROV2 = 4.02 MΩ, RUV1= 5.6 MΩ, RUV2 = 4.42 MΩ, ROC1= 15.62 MΩ, ROC2 = 4.42 MΩ
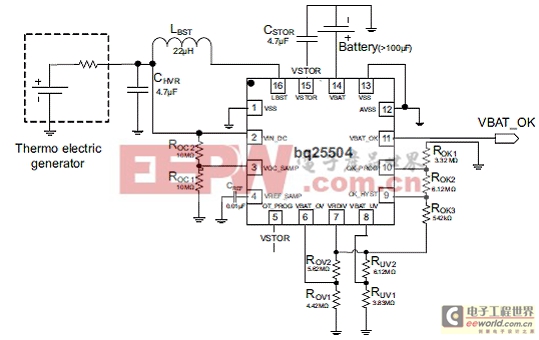
圖3.bq25504 TEG應(yīng)用電路圖
VIN_DC = 0.5 V, CSTOR = 4.7 μF, LBST = 22 μH, CHVR = 4.7 μF, CREF = 10 nF, TSD_PROTH (120°C), MPPT (VOC) = 50% VBAT_OV = 4.2 V, VBAT_UV = 3.2 V, VBAT_OK = 3.5 V, VBAT_OK_HYST = 3.7 V, ROK1 = 3.32 MΩ, ROK2 = 6.12 MΩ, ROK3 = 0.542 MΩ, ROV1 = 4.42 MΩ, ROV2 = 5.62 MΩ, RUV1 = 3.83 MΩ, RUV2 = 6.12 MΩ, ROC1 = 10 MΩ, ROC2 = 10 MΩ
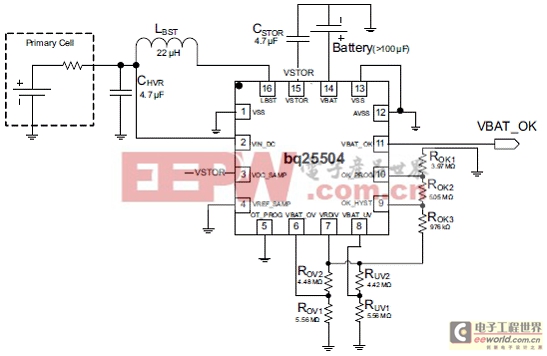
圖4.bq25504 MPPT應(yīng)用電路圖
VIN_DC = 1.2 V, CSTOR = 4.7 μF, LBST = 22 μH, CHVR = 4.7 μF, TSD_PROTL (65℃),
MPPT (VOC) = Disabled VBAT_OV = 3.3 V, VBAT_UV = 2.2 V, VBAT_OK = 2.8 V, VBAT_OK_HYST = 3.1 V,ROK1 = 3.97 MΩ, ROK2 = 5.05 MΩ, ROK3 = 0.976 MΩ, ROV1 = 5.56 MΩ, ROV2 = 4.48 MΩ, RUV1 = 5.56 MΩ, RUV2 = 4.42 MΩ
bq25504 EVM評估板
bq25504 EVM – Ultra Low Power Boost Converter with Battery Management for Energy Harvester Applications
bq25504EVM-674 – Ultra Low Power Boost Converter with Battery Management for Energy Harvester Applications. This EVM is programmed from the factory for settings compatible with most MCU’s and 3V coin cell batteries. The EVM is programmed to deliver a 3.1VDC maximum voltage (OV) for charging the storage element and the under voltage is programmed to 2.2VDC. The VBAT_OK indication toggles high when VSTOR ramps up at 2.8VDC and when VSTOR ramps down to 2.4VDC. The user’s guide describes the bq25504 evaluation module (EVM), how to perform a stand-alone evaluation and allows the EVM to interface with the system and host.
bq25504 EVM評估板主要特性:
Evaluation Module for bq25504
Ultra Low Power Boost Converter/Charger with Battery Management for Energy Harvester Applications
Resistor-programmable settings for under voltage, over voltage for flexible battery management Including POTs for fine tuning the settings (not populated)
Programmable push-pull output Indication for battery status (VBAT_OK)
Test Points for Key Signals Available for Testing Purpose – Easy Probe Hook-up Jumpers Available – Easy to Change Settings

圖5. bq25504 EVM評估板外形圖
bq25504 EVM評估板性能指標(biāo):
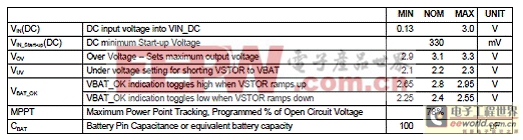
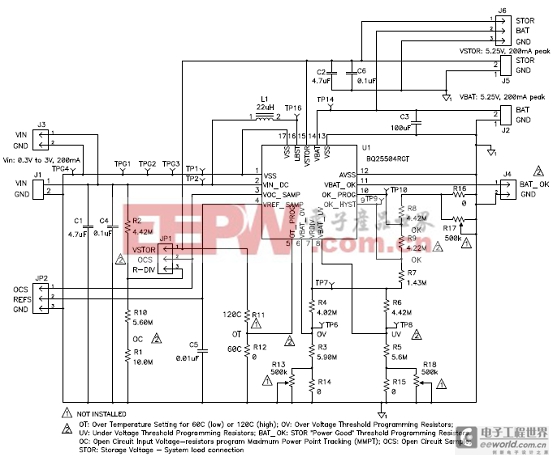
圖6. bq25504 EVM評估板電路圖
bq25504 EVM評估板材料清單(BOM):
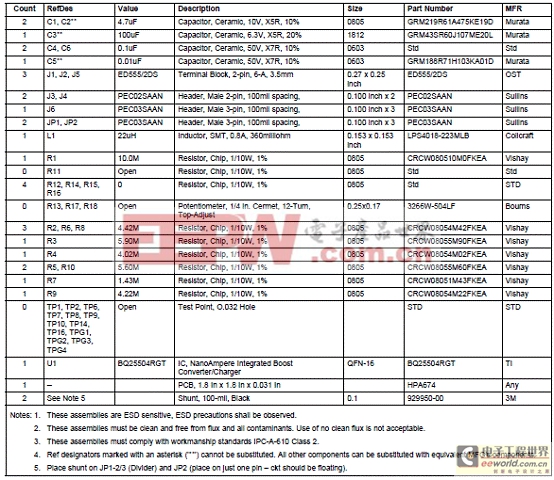
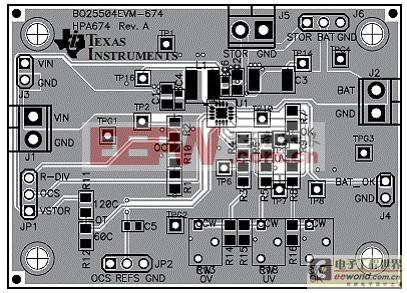
圖7. bq25504 EVM評估板PCB布局圖
TI 太陽能能量采集總體解決方案
傳統(tǒng)逆變器解決方案
Central, or “traditional”, inverters are centralized power control units that convert DC power from a string of 72-cell solar panels to AC power for use on the electrical utility grid. These are usually large scale commercial or residential systems producing in excess of 1 kW of power. Maximum power point tracking for the entire string is done only at the inverter box, which may also include relays to “island” the solar system from the grid.
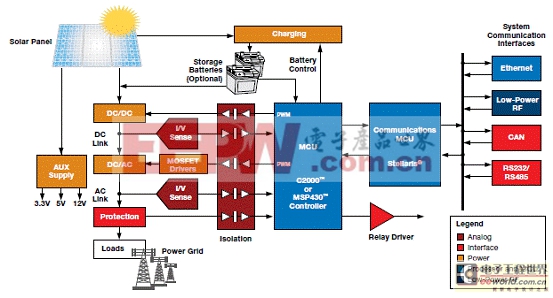
圖8.. 傳統(tǒng)逆變器解決方案框圖
微逆變器解決方案
Micro-inverters operate similarly to central inverter systems, but are installed on each individual panel and handle much less
power, typically 300 W. Micro-inverters provide the benefit of scalability for those who want to start small, yet have full
DC/AC conversion with MPPT, and expand later.
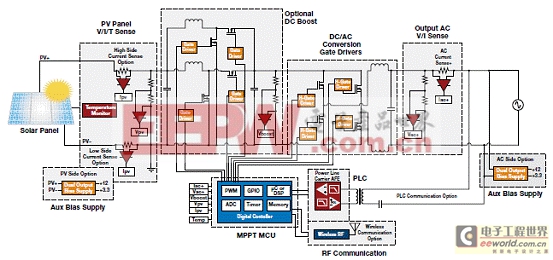
圖9.微逆變器解決方案框圖(1)
Micro-converters maximize the DC power point of a single solar panel and convert (down or up) the DC voltage to be transported downstream to a centralized AC (grid-tied) inverter. Being located on each panel, these systems are lower power (typ. 300 W) than centralized converters. These are sometimes called “optimizers” because they optimize the power of each panel, increasing the overall efficiency of the system.
?
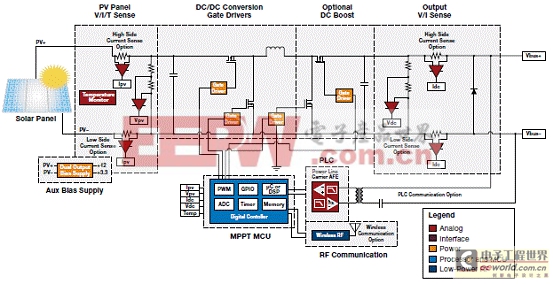
圖10.微逆變器解決方案框圖(2)
3.電池充電解決方案
Off-grid solar power systems often need to charge a battery, or array of battery cells, that provide continuous power to the load when solar energy is no longer present. Often cost sensitive, in order to optimize the size, cost and usable power of the storage elements, off-grid systems also require that the power point be maximized. However, this can be done by employing, lower power and less complex MCUs than grid-tied systems or by employing a simple fixed power point – often set at 76% of VOC. Loads such as LED lighting and motors may require additional power boosting and/or control.
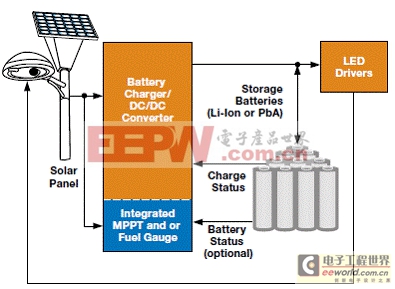
圖11.太陽能街燈照明方框圖.
詳情請見:
http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/bq25504.pdf
和
http://www.ti.com/lit/ug/sluu654a/sluu654a.pdf
以及
ht













評論